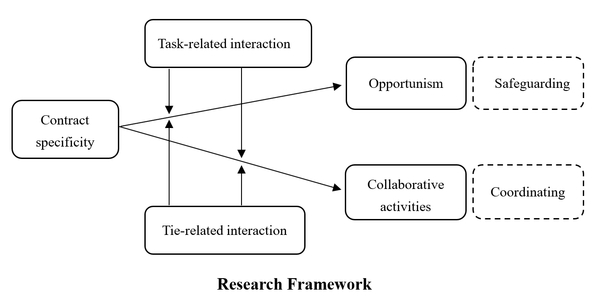
Social media has been increasingly adopted in managing business relationships, which subsequently affects various aspects of channel relationships. However, an examination of different categories of social media-enabled interactions and how they might be utilized in the business-to-business context is lacking. Our study distinguishes two categories of social media-enabled interactions, namely task- and tie-related interactions, and explores the (mis)match between these two and firms’ use of contracts in achieving safeguarding and coordinating purposes in interfirm governance. Based on a survey of 504 manufacturers and the scenario-based experiment data, our results suggest the safeguarding effect of contract specificity is amplified by tie-related interactions, whereas the coordinating effect of contract specificity is strengthened by task-related interactions. Our study enriches the interfirm governance literature by uncovering the roles of these two types of interactions in matching contract specificity to achieve safeguarding and coordinating purposes, which provides actionable insights for managers in governing interfirm relationships.
If you are interested in the research, please read the paper:
Feng, C., Yu, J., Fan, Y. and Chen, H. (2025), Performance implications of match between social media–enabled interactions and contracts in interfirm governance, Internet Research, Vol. 35 No. 1, pp. 264-293.
Doi.org/10.1108/INTR-10-2022-0844
A full version of this article could be viewed at:
https://doi.org/10.1108/INTR-10-2022-0844

Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Copyright 2017 | All Rights Reserved with NUAA
